Class 11 Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs with Answer
Engaging in Class 11 Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs with answers serves as a valuable resource for Sainik School aspirants, providing a focused approach to mastering fundamental concepts. These multiple-choice questions are tailored to the class 11 chemistry syllabus, emphasizing the crucial topic of hydrogen. By incorporating clear answers, this resource aids in effective self-assessment, helping students identify their strengths and areas for improvement. The systematic practice of these MCQs not only enhances knowledge retention but also sharpens problem-solving skills, essential for success in the competitive Sainik School entrance exams.
As students prepare for Sainik School admissions, these MCQs offer a strategic tool to reinforce their understanding of hydrogen-related principles. Beyond exam readiness, this resource aligns with the school’s commitment to holistic education, fostering a comprehensive grasp of chemistry concepts and preparing students for the challenges of both the entrance exams and future academic pursuits.
1. Dihydrogen can be prepared on commercial scale by different methods. In its preparation by the action of steam on
hydrocarbons, a mixture of CO and H gas is formed. It is known as _.
- Water gas
- Syngas
- Producer gas
- Industrial gas
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. Water gas
- Syngas
Q2. Hydrogen is evolved by reaction of cold HNO3 (5%) on:
- Fe
- Cu
- Mn
- Al
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 3. Mn
Q3. In which of the following respect, electronic configuration of hydrogen has resemblance to alkali metals and halogens
respectively?
- It lose one electron to form unipositive ion and gain one electron to form uninegative ion.
- It gain one electron to form uninegative ion and lose one electron to form unipositive ion.
- It has the ability only to gain one electron.
- None of the above.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. It lose one electron to form unipositive ion and gain one electron to form uninegative ion
Q4. Interstitial hydride can be formed by:
- Na
- K
- Fe
- Ca
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 3. Fe
Q5. The decomposition of H2 O2 is prevented by:
- MnO2
- NaOH.
- Acetanilide.
- Oxalic acid.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 3. Acetanilide.
Q6. Which of the following ions will cause hardness in water sample?

Click To View The Answer
Ans: 4. Ca2+
Q7. Which of the following compounds is used for water softening?
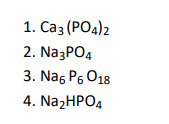
Click To View The Answer
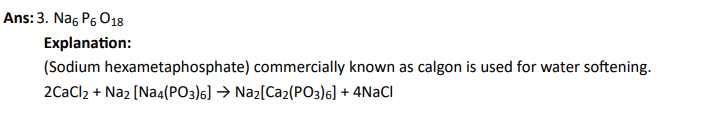
Q8. Which of the following hydrides is electron-precise hydride?
- B2 H6
- NH3
- H2 O
- CH4
Click To View The Answer
Ans.4.CH4
Q9. Which of the following properties of dihydrogen is incorrect?
1.It is colourless, odourless, tasteless.
- It is combustible gas.
- It is lighter than air.
- It is soluble in water.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 4. It is soluble in water.
Q10. Where is false about H2 O2 ?
- It acts as both oxidising and reducing agent.
- Two OH bonds lie in same plane.
- It is pale blue liquid.
- It can be oxidised by O3
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 2. Two OH bonds lie in same plane.
Q11. Advantage of hydrogen economy is the:
- Transmission of energy in the form of electric power.
- Transmission of energy in the form of chemical energy.
- Transmission of energy in the form of dihydrogen and not as electric power.
- Transmission of mechanical energy
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 3. Transmission of energy in the form of dihydrogen and not as electric power.
Q12. Why does H ion always get associated with other atoms or molecules?
- Ionisation enthalpy of hydrogen resembles that of alkali metals.
- Its reactivity is similar to halogens.
- It resembles both alkali metals and halogens.
- Loss of an electron from hydrogen atom results in a nucleus of very small size as compared to other atoms or ions.
Due to small size it can not exist freely
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 4. Loss of an electron from hydrogen atom results in a nucleus of very small size as compared to other atoms or ions. Due to small size it can
not exist freely.
Q13. The isotopes of hydrogen have the same electronic configurations and chemical properties. The only difference is in
their rates of reaction. It is mainly due to their different:
- Enthalpy of fusion.
- Enthalpy of vaporisation.
- Bond dissociation enthalpy.
- Atomic mass.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 3. Bond dissociation enthalpy.
Q14. Which of the following is not an example of ionic hydride:
- CaH2 .
- CsH.
- CeH2
Click To View The Answer
CeH2
Q15. Hardness of water may be temporary or permanent. Permanent hardness is due to the presence of:
- Chlorides of Ca and Mg in water.
- Sulphate of Ca and Mg in water.
- Hydrogen carbonates of Ca and Mg in water.
- Carbonates of alkali metals in water
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. Chlorides of Ca and Mg in water.
- Sulphate of Ca and Mg in water
FAQs
Q: How do Class 11 Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs with answers contribute to effective exam preparation for Sainik School aspirants?
A: Engaging with Hydrogen MCQs provides Sainik School candidates with a targeted method to consolidate their understanding of fundamental chemistry concepts. These questions, specifically tailored to the class 11 syllabus, offer clear and concise answers, facilitating self-assessment. The practice of these MCQs not only reinforces knowledge but also sharpens problem-solving skills, essential for success in the competitive Sainik School entrance exams. By focusing on the topic of hydrogen, students gain a comprehensive understanding, ensuring they are well-prepared for the specific content covered in the exams.
Q: How does the inclusion of Class 11 Chemistry Hydrogen MCQs align with Sainik School’s emphasis on holistic education?
A: Integrating Hydrogen MCQs into the study material aligns with Sainik School’s commitment to holistic education. Beyond exam preparation, these questions foster a deeper understanding of the principles related to hydrogen, a fundamental element in chemistry. The inclusion of clear answers ensures that students not only acquire theoretical knowledge but also develop strong problem-solving skills. This approach prepares Sainik School aspirants not just for the entrance exams but also instills a broader appreciation for chemistry concepts, contributing to their overall academic growth and success.
