Class 11 Organic Chemistry MCQs with Answers
Class 11 Organic Chemistry MCQs with Answers offer a targeted and comprehensive approach for Sainik School aspirants preparing for their chemistry exams. These multiple-choice questions are specifically tailored to the class 11 chemistry syllabus, focusing on organic chemistry principles. With clear and concise answers provided, students benefit from efficient self-assessment, identifying strengths and areas for improvement. Organic chemistry is a foundational aspect of the curriculum, and these MCQs ensure a solid understanding of key concepts.
As students gear up for Sainik School entrance exams, practicing these MCQs not only aids in exam readiness but also enhances problem-solving skills crucial for success. The content aligns with the broader goals of Sainik School education, promoting a holistic understanding of organic chemistry principles. This resource serves as an invaluable tool, helping students build a strong foundation for future academic endeavors and meeting the specific requirements of Sainik School examinations.
Q1.
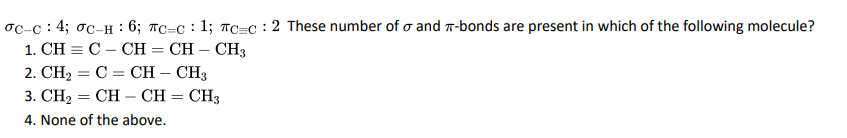
Click To View The Answer
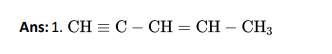
Q2. Sodium nitroprusside reacts with sodium sulphide formed in lassaigne’s test to detect presence of sulphur gives violet colour
due to:
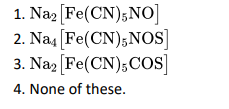
Click To View The Answer
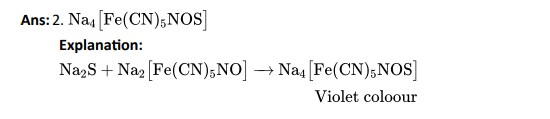
Q3. Which of the following compounds contain all the carbon atoms in the same hybridisation state?
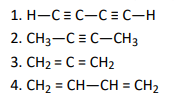
Click To View The Answer
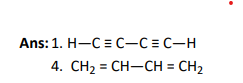
Q4.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. I shows +R-effect, whereas II shows -R-effect.
Q5. The principle involved in paper chromatography is:
- Adsorption
- Partition
- Solubility
- Volatility
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 2. Partition
Q6. Electronegativity of carbon atoms depends upon their state of hybridisation. In which of the following compounds, the
carbon marked with asterisk is most electronegative?
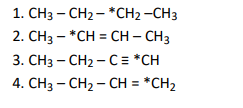
Click To View The Answer
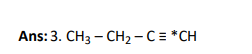
Q7.

Click To View The Answer
Ans: 4. Hydrolysis agent.
Q8. In Dumas method, 0.25g of organic compound gave 40ml of N, at 300k and 725mm pressure. If aqueous tension at 300k is
25mm, the percentage of nitrogen in compound is:
- 16.76%
- 15.76%
- 17.36%
- 18.20%
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. 16.76%
Q9. Name the two types of chromatography techniques based on the principle of differential adsorption.
- Column chromatography and thick layer chromatography.
- Non-column chromatography and thin layer chromatography.
- Column chromatography and thin layer chromatography.
- Paper chromatography and thick layer chromatography.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 3. Column chromatography and thin layer chromatography.
Explanation:
Two types of adsorption chromatography techniques are column chromatography and thin layer chromatography.
Q10. Hyperconjugation involves delocalisation of _.
- Electrons of carbon-hydrogen σ bond of an alkyl group directly attached to an atom of unsaturated system.
- Electrons of carbon-hydrogen σ bond of alkyl group directly attached to the positively charged carbon atom.
- -Electrons of carbon-carbon bond.
- Lone pair of electrons.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. Electrons of carbon-hydrogen σ bond of an alkyl group directly attached to an atom of unsaturated system.
- Electrons of carbon-hydrogen σ bond of alkyl group directly attached to the positively charged carbon atom.
Q11. The number of structural isomers possible for the molecular formula = C3 H9 N is:
- 4
- 5
- 2
- 3
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. 4
Q12. In which of the following, functional group isomerism is not possible?
- Alcohols
- Aldehydes
- Alkyl halides
- Cyanides
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 3. Alkyl halides
Q13. The difference in energy between the actual structure and lowest energy canonical form is called:
- Resonance energy.
- Localisation energy.
- Both (a) and (b).
- All of these.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. Resonance energy.
Q14. Glycerol can be separated from spent-lye in soap industry by:
- Chromatography.
- Sublimation.
- Fractional distillation.
- Distillaltion under reduced pressure.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 4. Distillaltion under reduced pressure.
Explanation:
Glycerol decomposes at its boiling point is separated from spent-lye by using distillation under reduced pressure.
Q15. What is the technological applications of fractional distillation?
- To separate different fractions of crude oil in petroleum industry.
- To separate different fractions of volatile and non-volatile solvents.
- To separate mixture of amino acids.
- No technological application of fractional distillation.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. To separate different fractions of crude oil in petroleum industry.
FAQs
Q: How can Class 11 Organic Chemistry MCQs benefit Sainik School aspirants in their exam preparation?
A: Engaging with Organic Chemistry MCQs tailored for class 11 ensures that Sainik School candidates have a targeted study approach. These questions cover essential organic chemistry principles and provide clear answers for efficient self-assessment. By practicing these MCQs, students not only reinforce their understanding but also develop strong problem-solving skills, a key aspect of succeeding in the competitive Sainik School entrance exams. The focus on organic chemistry aligns with the curriculum, ensuring that aspirants are well-prepared for the specific content they will encounter in the examinations.
Q: How does the inclusion of Class 11 Organic Chemistry MCQs support a holistic education approach at Sainik School?
A: The incorporation of Organic Chemistry MCQs into the study material reflects Sainik School’s commitment to holistic education. Beyond exam preparation, these questions foster a deeper understanding of organic chemistry principles, contributing to a well-rounded education. The clear answers provided not only help in grasping theoretical concepts but also promote effective problem-solving skills. This aligns with Sainik School’s broader goal of nurturing individuals with a comprehensive academic foundation, ensuring that students are not only successful in the entrance exams but also well-equipped for future academic pursuits
