Class 11 Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure MCQs with Answers
At Sainik School, our Class 11 Chemistry MCQs on “Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure” provide students with a comprehensive platform to master this essential topic. Covering various aspects of chemical bonding, molecular structure, and intermolecular forces, these multiple-choice questions offer thorough preparation for Class 11 Chemistry exams.
Our MCQs challenge students to apply their knowledge of chemical bonding and molecular structure to solve problems and analyze scenarios, fostering critical thinking and analytical skills essential for success in exams. Each MCQ is accompanied by a detailed answer explanation, enabling students to grasp the underlying concepts thoroughly.
By practicing Class 11 Chemistry MCQs on “Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure” at Sainik School, students not only prepare effectively for their exams but also gain a deeper understanding of the principles governing chemical bonding, molecular geometry, and the properties of substances, laying a strong foundation for their future studies and careers in chemistry and related fields.
Q1. Which of the following molecule has net dipole moment zero?
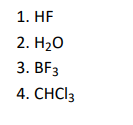
Click To View The Answers

Q2. Diagonal hybridisation is the another name of:

Click To View The Answers
Ans: 3. sp-hybridisation.
Explanation:
The sp-hybridisation is also called diagonal hybridisation.
Q3. In the following questions two or more options may be correct:
Which of the following have identical bond order?

Click To View The Answers
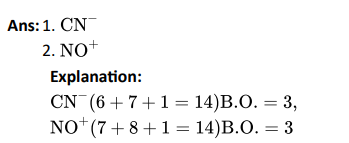
Q4. Predict the correct order:
- bp – bp > lp – bp > lp – bp (where bp is bonded paper and lp is lone pair of electrons)
- lp – bp > bp – bp > lp – lp
- lp – lp > lp – bp > bp – bp
- lp – lp > bp – bp > lp – bp
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 3. lp – lp > lp – bp > bp – bp
Q5. Lewis postulated that atoms achieve the stable octet when they are linked by:
- Ionic bonds.
- Covalent bonds.
- Coordinate bonds.
- Chemical bonds.
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 4. Chemical bonds.
Explanation:
The atoms can achieve the stable octet when they are linked by chemical bonds. It was postulated by Lewis.
Q6.
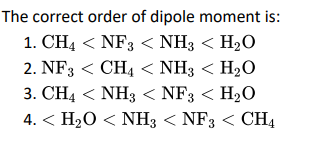
Click To View The Answers

Q7. Which of the following statements is correct?
- In the formation of dioxygen from oxygen atoms 10 molecular orbitals will be formed.
- All the molecular orbitals in the dioxygen will be completely filled.
- Total number of bonding molecular orbitals will not be same as total number of anti bonding orbitals in
dioxygen. - Number of filled bonding orbitals will be same as number of filled anti bonding orbitals.
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 1. In the formation of dioxygen from oxygen atoms 10 molecular orbitals will be formed.
Q8. Canonical forms:
- Have real existence.
- Have no real existence.
- Are present in equilibrium.
- Exist in one form for certain frClick To View The Answersaction of time and to other in remaining time.
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 2. Have no real existence.
Q9

Click To View The Answers
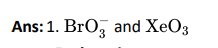
Q10. Which of the following molecules represents resonance?

Click To View The Answers
Ans: 4. All of these.
Q11. Amongst the following elements, whose electronic configurations are given below, the one having the highest
ionization enthalpy is

Click To View The Answers

Q12. In the following questions two or more options may be correct:
Which of the following attain the linear structure:

Click To View The Answers

Q13. The boiling point of a substance increases with increase in:
- Intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
- Intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
- Molecular mass.
- Both (a) and (c).
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 4. Both (a) and (c).
Q14. Why do the deviations occur from idealized shape of H O and NH molecules?
- Same hybridisation.
- Different hybridisation.
- Repulsive effect.
- None of these.
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 3. Repulsive effect.
Q15. The bond between B and C will be:
- Ionic
- Covalent
- Hydrogen
- Coordinate
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 2. Covalent
Explanation:
Both B and C are non-metals so, the bond formed between them will be covalent.
FAQs
How do MCQs on “Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure” in Class 11 Chemistry assist students in understanding the different types of chemical bonds and their properties?
MCQs on “Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure” serve as valuable tools for Class 11 Chemistry students to comprehend the principles governing various types of chemical bonds such as covalent, ionic, and metallic bonds. These MCQs cover topics such as bond formation, bond length, bond angle, and bond polarity. By engaging with these MCQs, students can deepen their understanding of the characteristics and properties of different types of chemical bonds, enabling them to analyze and solve problems related to chemical bonding effectively
What strategies can students employ to effectively prepare for Class 11 Chemistry exams using MCQs on “Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure”?
To effectively prepare for exams using MCQs on “Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure,” students should first ensure a solid understanding of the fundamental concepts and principles within chemical bonding. They can then practice solving a variety of MCQs from reputable sources, focusing on different aspects such as bond types, bond properties, and molecular geometry. It’s essential to analyze both correct and incorrect answers to deepen understanding and identify areas for improvement. Additionally, students can use MCQs to simulate exam conditions, helping them become familiar with the format and timing of the actual examination. Regular practice with MCQs, coupled with comprehensive revision of concepts, can significantly enhance students’ performance in Class 11 Chemistry exams.
