Class Chemistry 11 Equilibrium MCQs with Answer
Engaging in Class 11 Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs with answers is a valuable strategy for Sainik School aspirants seeking proficiency in chemistry concepts. These multiple-choice questions are meticulously designed to align with the class 11 curriculum, specifically focusing on the equilibrium topic. By incorporating a range of questions and clear answers, this resource serves as an effective aid for students preparing for their Sainik School exams. Mastering equilibrium principles is crucial for understanding chemical reactions, and these MCQs provide a targeted approach to reinforce comprehension.
As candidates gear up for Sainik School entrance exams, practicing these MCQs not only aids in self-assessment but also enhances problem-solving skills and exam readiness. The content is tailored to the class 11 chemistry syllabus, ensuring relevance and applicability for students navigating the Sainik School admission process. In addition to academic excellence, this resource fosters a deeper understanding of equilibrium dynamics, contributing to a well-rounded education.
Q1. Which of the following is an example of a reversible reaction?
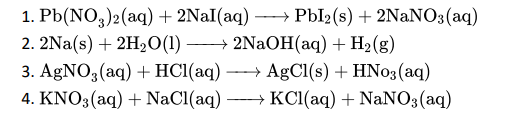
Click To View The Answer
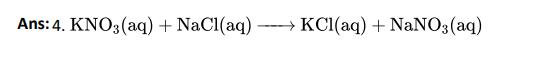
Q2. What is pH of resulting solution when equal volume when equal of 0.1M NaOH and 0.01M HCl are mixed?
- 7
- 1.04
- 12.65
- 2.0
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 3. 12.65
Q3. The pH of neutral water at 25°C is 7.0. As the temperature increases, ionisation of water increases, however, the
concentration of H+ ions and OH– ions are equal. What will be the pH of pure water at 60°C?
- Equal to 7.0
- Greater than 7.0
- Less than 7.0
- Equal to zero.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 3. Less than 7.0
Q4.
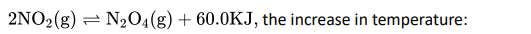
- Favour the formation of N2O4 .
- Favour the decomposition of N2O4
- Does not affect the equilibrium.
- Stops the process.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 2. Favour the decomposition of N2O4
Q5. What will be the correct order of vapour pressure of water, acetone and ether at 30°C. Given that among these
compounds, water has maximum boiling point and ether has minimum boiling point?
1. Water < ether < acetone.
2. Water < acetone < ether.
3. Ether < acetone < water.
4. Acetone < ether < water.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 2. Water < acetone < ether.
Q6. On increasing the pressure, in which direction will the gas phase reaction proceed to re-establish equilibrium, is
predicted by applying the Le Chatelier’s principle. Consider the reaction.
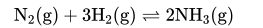
Which of the following is correct, if the total pressure at which the equilibrium is established, is increased without
changing the temperature?
- K will remain same.
- K will decrease.
- K will increase.
- K will increase initially and decrease when pressure is very high.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. K will remain same.
Q7. The solubility product of a sparingly soluble salt AB at room temperature is 1.21 × 10-6 , its molar solubility is:
- 1.21 × 100M.
- 1.1 × 10-4 M.
- 1.1 × 10-3 M.
- None of these.
Click To View The Answer
Ans.3. 1.1 × 10-3 M.
Q8. The concentration of hydrogen ion in a sample of soft drink is 3.8 × 10-3 M. What is its pH?
- 4.32
- 5.12
- 3.31
- 2.42
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 4. 2.42
Q9. Which of the following is not a general characteristic of equilibria involving physical processes?
1.Equilibrium is possible only in a closed system at a given temperature.
- All measurable properties of the system remain constant.
- All the physical processes stop at equilibrium.
- The opposing processes occur at the same rate and there is dynamic but stable condition.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 3. All the physical processes stop at equilibrium.
Explanation:
All the physical processes like melting of ice and freezing of water, etc., do not stop at equilibrium.
Q10.
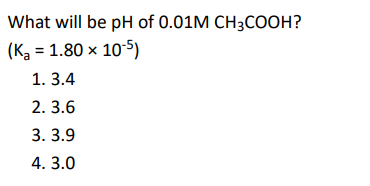
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. 3.4
Q11. A 0.2 molar solution of formic acid is 3.2% ionised. Its ionisation constant is:
- 9.6 × 10-3
- 2.1 × 10-4
- 1.25 × 10-6
- 4.8 × 10-5
Click To View The Answer
Ans.2. 2.1 × 10-4
Q12. Which one of the following informations can be obtained on the basis of Le-Chatelier principle?
- Dissociation constant of a weak acid.
- Entropy change in a reaction.
- Equilibrium constant of a chemical reaction.
- All of the above.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 4. All of the above.
Q13. At a particular temperature and atmospheric pressure, the solid and liquid phases of a pure substance can exist in
equilibrium. Which of the following term defines this temperature?
- Normal melting point.
- Equilibrium temperature.
- Boiling point.
- Freezing point.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. Normal melting point.
- Freezing point.
Q14. Hydronium ion concentration in molarity is more conveniently expressed on a logarithmic scale known as the:
- pH scale.
- pOH scale.
- Ionic product of water.
- Both (a) and (b).
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. pH scale.
Q15. Which of the following is correct regarding buffer sol?
- It contains a weak acid and its conjugate base.
- It contains a weak base and its conjugate acid.
- It shows little change in pH on adding small amount of acid or base.
- None of the above
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 3. It shows little change in pH on adding small amount of acid or base.
FAQs
Q: How can practicing Class 11 Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs with answers contribute to better performance in Sainik School entrance exams?
A: Engaging with these MCQs offers Sainik School aspirants a targeted approach to mastering equilibrium concepts. The questions are aligned with the class 11 chemistry syllabus, ensuring that students are well-prepared for the specific topics covered in the entrance exams. By providing clear and concise answers, this resource facilitates self-assessment and helps identify areas of improvement. The systematic practice of these MCQs not only reinforces knowledge but also enhances problem-solving skills, providing a competitive edge for success in the Sainik School admission process.
Q: How does the inclusion of Class 11 Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs with answers support a comprehensive understanding of chemistry principles for Sainik School students?
A: Integrating MCQs on equilibrium into the study material caters to the Sainik School’s commitment to holistic education. Beyond exam preparation, these questions foster a deeper understanding of chemical equilibrium principles, a fundamental aspect of chemistry. The inclusion of clear answers ensures that students not only grasp the theoretical concepts but also develop strong problem-solving skills. This approach aligns with Sainik School’s goal of nurturing well-rounded individuals with a solid academic foundation, preparing them for success in both the entrance exams and future academic endeavors.
