Class 11 Chemistry Redox Reaction MCQs with Answers
Class 11 Chemistry Redox Reaction MCQs with Answers cater to the specific needs of Sainik School aspirants, providing a focused approach to mastering redox reaction principles. Tailored to the class 11 chemistry syllabus, these multiple-choice questions offer clear and concise answers, facilitating effective self-assessment. As redox reactions are foundational in chemistry, this resource ensures a solid grasp of essential concepts.
As students prepare for Sainik School entrance exams, engaging with these MCQs not only enhances exam readiness but also sharpens critical thinking and problem-solving skills. The content aligns with the broader goals of Sainik School education by promoting a comprehensive understanding of redox reactions. By emphasizing clear answers, this resource aids students in identifying areas for improvement, contributing to a holistic approach to exam preparation. Sainik School aspirants benefit from a well-rounded educational experience, preparing them for success in both the entrance exams and future academic pursuits.
Q1. Identify the correct statement (s) in relation to the following reaction:
Zn + 2HCl −−→ ZnCl2 + H2
- Zinc is acting as an oxidant.
- Chlorine is acting as a reductant.
- Hydrogen ion is acting as an oxidant.
- Zinc is acting as a reductant.
Click To View The Answer
: 3. Hydrogen ion is acting as an oxidant.
- Zinc is acting as a reductant.
Q2. Which of the following elements does not show disproportionation tendency?
- Cl
- Br
- F
- I
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 3. F
Q3. The exhibition of various oxidation states by an element is also related to the outer orbital electronic
configuration of its atom. Atom(s) having which of the following outermost electronic configurations will exhibit
more than one oxidation state in its compounds:
- 3s1
- 3d14s2
- 3d24s2
- 3s23p3
Click To View The Answer
Ans. 3. 3d14s2
4. 3d24s2
5.3s23p3
Q4. Which of the following is not an example of redox reaction?
- CuO + H2 −−−→ Cu + H2O
- Fe2O3 + 3CO −−−→ 2Fe + 3CO2
- 2K + F2 −−→ 2KF
- BaCl2 + H2SO4 −−→ BaSO4 + 2HCl
Click To View The Answer
Ans:4. BaCl2 + H2SO4 −−→ BaSO4 + 2HCl
Q5. Which of the following metal displacement reaction will not take place and why?
- Cu + Mg2+ −−→
- Mg + Cu2+ −−→
- Pb + Ag+ −−→
- Zn + Cu2+ −−→
Click To View The Answer
Ans:1. Cu + Mg2+ −−→
Q6. In which of the following groups of iodine compounds shows increasing order of oxidation states:
- HlO4, ICl, I2, Hl
- Hl, I2, IC, HIO4
- I2, HI, HIO4 HI
- ICl HIO4,HI, I2
Click To View The Answer
Ans:1. Hl, I2, IC, HIO4
Q7. Which of the following is a redox reaction (disproportionation reaction).
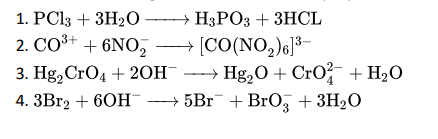
Click To View The Answer
Ans:4. 3Br2 + 6OH− −−→ 5Br− + BrO−3 + 3H2O
Q8 . The reaction, 2H2O(I) −− Δ−→2H2(g) + O2(g) is an example of:
- Addition reaction.
- Decomposition reaction.
- Displacement reaction.
- None of these.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 2. Decomposition reaction.
Q9. The given reactions such as:
- Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
- Fe + 2HCl → FeCl2 + H2
Are represented as:
- Displacement of zinc and iron metals.
- Displacement of only zinc metals.
- Displacement of only iron metals.
- Displacement of hydrogen.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 4. Displacement of hydrogen.
Q10. Identify disproportionation reaction:
- CH4 + 2O2 −−→ CO2 + 2H2O
- CH4 + 4Cl2 −−→ CCl4 + 4HCl
- 2F2 + 2OH− −−→ 2F− + OF2 + H2O
- 2NO2 + 2OH− −−→ NO−2 + NO−3 + H2O
Click To View The Answer
Ans:4. 2NO2 + 2OH− −−→ NO−2 + NO−3 + H2O
Q11. The rods of transition metals such as copper and zinc where potential difference is generated, are termed as:
- Electrodes.
- Cathodes.
- Anodes.
- None of these.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. Electrodes.
Q12. Which of the following electrodes will act as anodes, when connected to Standard Hydrogen Electrode?
- Al/Al3+;E⊖ = −1.66
- Fe/Fe3+;E⊖ = −0.44
- Cu/Cu2+;E⊖ = −0.34
- F2(g)/2F−(aq);E⊖ = +2.87
Click To View The Answer
Q13. Which of the following pairs of ions cannot coexist in aqueous solution?
- Cr2+and MnO−4
- Fe3+and Cr2O2−7
- Cr2+and I−3
- Mn2+and Cl−
Click To View The Answer
Q14. Which of the following reactions represent(s) redox process?
- Electrochemical process for extraction of highly reactive metals and non-metals.
- Manufacturing of caustic soda.
- Corrosion of metals.
- All of the above.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 4. All of the above.
Explanation:
Electrochemical processes for the extraction of highly reactive metals and non-metals, manufacturing of chemical compounds like
caustic soda, operation of dry and wet batteries and corrosion of metals fall within the range of redox processes.
Q15. The given reaction,CuSO4 + Zn → Cu + ZnSO4 is an example of:
- Metal displacement reaction.
- Non-metal displacement reaction.
- Metal addition reaction.
- Non-metal addition reaction.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. Metal displacement reaction.
FAQs
Q: How do Class 11 Chemistry Redox Reaction MCQs with Answers assist Sainik School aspirants in their exam preparation?
A: Engaging with Redox Reaction MCQs designed for class 11 ensures that Sainik School candidates have a targeted study resource. These questions cover key redox reaction principles and provide clear answers, facilitating efficient self-assessment. Aspirants benefit not only by reinforcing their understanding of redox reactions but also by honing problem-solving skills essential for success in the competitive Sainik School entrance exams. The focus on redox reactions aligns with the curriculum, ensuring that students are well-prepared for the specific content tested in the examinations.
Q: How does the inclusion of Class 11 Chemistry Redox Reaction MCQs contribute to a comprehensive education approach at Sainik School?
A: Integrating Redox Reaction MCQs into the study material reflects Sainik School’s commitment to a holistic education. Beyond exam preparation, these questions foster a deeper understanding of redox reaction principles, contributing to a well-rounded education. The clear answers provided not only aid in grasping theoretical concepts but also promote effective problem-solving skills. This aligns with Sainik School’s broader goal of nurturing individuals with a comprehensive academic foundation, ensuring that students are not only successful in the entrance exams but also well-equipped for future academic pursuits.
