Class 12 Chemistry Solutions MCQs with Answers
At Sainik School, our Class 12 Chemistry MCQs on “Solutions” provide students with a comprehensive platform to master this fundamental topic. Covering various aspects of solutions, including types of solutions, colligative properties, solubility, and concentration units, these multiple-choice questions offer thorough preparation for Class 12 Chemistry exams.
Our MCQs challenge students to apply their knowledge of solution chemistry to solve problems and analyze scenarios, fostering critical thinking and analytical skills essential for success in exams. Each MCQ is accompanied by a detailed answer explanation, enabling students to grasp the underlying concepts thoroughly.
By practicing Class 12 Chemistry MCQs on “Solutions” at Sainik School, students not only prepare effectively for their exams but also gain a deeper understanding of the principles governing solution behavior, equipping them with essential skills for their academic pursuits and future careers in science and technology.
Q1. The value of Henry’s constant K is _.
- Greater for gases with higher solubility.
- Greater for gases with lower solubility.
- Constant for all gases.
- Not related to the solubility of gases.
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 2. Greater for gases with lower solubility
Q2. Which of the following statements is false?
- Two different solutions of sucrose of same molality prepared in different solvents will have the same
depression in freezing point. - The osmotic pressure of a solution is given by the equation (where C is the molarity of the
solution). - Decreasing order of osmotic pressure for 0.01M aqueous solutions of barium chloride, potassium chloride,
acetic acid and sucrose is BaCl2 > KCl > CH3 COOH > sucrose. - According to Raoult’s law, the vapour pressure exerted by a volatile component of a solution is directly
proportional to its mole fraction in the solution.
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 1. Two different solutions of sucrose of same molality prepared in different solvents will have the same depression in freezing point.
Q3. On the basis of information given below mark the correct option.
Information: On adding acetone to methanol some of the hydrogen bonds between methanol molecules break.
- At specific composition methanol-acetone mixture will form minimum boiling azeotrope and will show
positive deviation from Raoult’s law. - At specific composition methanol-acetone mixture forms maximum boiling azeotrope and will show positive
deviation from Raoult’s law. - At specific composition methanol-acetone mixture will form minimum boiling azeotrope and will show
negative deviation from Raoult’s law. - At specific composition methanol-acetone mixture will form maximum boiling azeotrope and will show
negative deviation from Raoult’s law.
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 1. At specific composition methanol-acetone mixture will form minimum boiling azeotrope and will show positive deviation from
Raoult’s law.
Explanation:
At specific composition methanol-acetone mixture will show positive deviation from Raoulfs law as it has lesser interactions than
methanol- methanol and acetone-acetone interactions. Hence it forms minimum boiling azeotrope
Q4. The values of Van’t Hoff factors for KCl, NaCl and K2 SO4 , respectively, are __.
- 2, 2 and 2
- 2, 2 and 3
- 1, 1 and 2
- 1, 1 and 1
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 2. 2, 2 and 3
Q5. Colligative properties are observed when _.
- A non volatile solid is dissolved in a volatile liquid.
- A non volatile liquid is dissolved in another volatile liquid.
- A gas is dissolved in non volatile liquid.
- A volatile liquid is dissolved in another volatile liquid.
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 1. A non volatile solid is dissolved in a volatile liquid.
- A non volatile liquid is dissolved in another volatile liquid.
Q6. Isotonic solutions must have the same _.
- Solute.
- Density.
- Elevation in boiling point.
- Depression in freezing point.
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 3. Elevation in boiling point.
- Depression in freezing point.
Q8. Intermolecular forces between two benzene molecules are nearly of same strength as those between two
toluene molecules. For a mixture of benzene and toluene, which of the following are not true?

Click To View The Answers
Ans: 3. These will form minimum boiling azeotrope.
- These will not form ideal solution.
Q9. In isotonic solutions __.
- Solute and solvent both are same.
- Osmotic pressure is same.
- Solute and solvent may or may not be same.
- Solute is always same solvent may be different.
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 2. Osmotic pressure is same.
- Solute and solvent may or may not be same.
Q10. Which of the following statements is false?
- Units of atmospheric pressure and osmotic pressure are the same.
- In reverse osmosis, solvent molecules move through a semipermeable membrane from a region of lower
concentration of solute to a region of higher concentration. - The value of molal depression constant depends on nature of solvent.
- Relative lowering of vapour pressure, is a dimensionless quantity.
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 2. In reverse osmosis, solvent molecules move through a semipermeable membrane from a region of lower concentration of solute to
a region of higher concentration.
Q11. Which of the following aqueous solutions should have the highest boiling point?

Click To View The Answers

Q12. On dissolving sugar in water at room temperature solution feels cool to touch. Under which of the following cases
dissolution of sugar will be most rapid?
- Sugar crystals in cold water.
- Sugar crystals in hot water.
- Powdered sugar in cold water.
- Powdered sugar in hot water.
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 4. Powdered sugar in hot water.
Q13. Value of Henry’s constant Kh __.
- Increases with increase in temperature.
- Decreases with increase in temperature.
- Remains constant.
- First increases then decreases.
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 1. Increases with increase in temperature.
Explanation:
Value of Henry’s constant increases with increase in temperature.
Q14. Consider the and mark the correct option.
- Water will move from side (A) to side (B) if a pressure lower than osmotic pressure is applied on piston (B).
- Water will move from side (B) to side (A) if a pressure greater than osmotic pressure is applied on piston (B).
- Water will move from side (B) to side (A) if a pressure equal to osmotic pressure is applied on piston (B).
- Water will move from side (A) to side (B) if pressure equal to osmotic pressure is applied on piston (A).
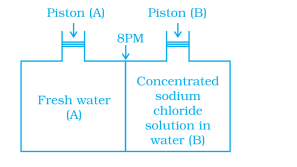
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 2. Water will move from side (B) to side (A) if a pressure greater than osmotic pressure is applied on piston (B).
Q15. Which of the following units is useful in relating concentration of solution with its vapour pressure?
- Mole fraction.
- Parts per million.
- Mass percentage.
- Molality.
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 1. Mole fraction.
FAQs
How do MCQs on “Solutions” in Class 12 Chemistry help students understand the properties and behavior of different types of solutions?
MCQs on “Solutions” serve as valuable tools for Class 12 Chemistry students to deepen their understanding of the properties and behavior of various types of solutions. These MCQs cover topics such as solubility, concentration, colligative properties, and factors affecting solubility. By engaging with these MCQs, students can analyze different scenarios involving solutions and apply their knowledge to solve problems effectively. This not only reinforces their understanding of solution chemistry but also enhances their critical thinking and analytical skills.
What strategies can students employ to effectively prepare for Class 12 Chemistry exams using MCQs on “Solutions”?
To effectively prepare for exams using MCQs on “Solutions,” students should first ensure a solid understanding of the fundamental concepts and principles governing solution behavior. They can then practice solving a variety of MCQs from reputable sources, focusing on different aspects such as types of solutions, colligative properties, and concentration units. It’s essential to analyze both correct and incorrect answers to deepen understanding and identify areas for improvement. Additionally, students can use MCQs to simulate exam conditions, helping them become familiar with the format and timing of the actual examination. Regular practice with MCQs, coupled with a comprehensive revision of concepts, can significantly enhance students’ performance in Class 12 Chemistry exams.
