Class 12: Principles of Inheritance and Variation MCQs: Inheritance is the term given to the process by which characters are passed from parents to offspring which forms the basis of heredity. Heredity is the process of passing down genetic traits from parents to offspring. The degree of difference in characters between a parent and offspring is called variation. All these are studied under genetics which deals with the study of inheritance and variation of characters passed from parents to offspring. The first proper documented study of this inheritance and variation was done by G.J. Mendel which is why he is considered the father of genetics.
Class 12 Biology Principles of Inheritance and Variation MCQ with Answer
Q1. It is said that Mendel proposed that the factor controlling any character is discrete and independent. This
proposition was based on the:
- Results of F3 generation of a cross.
- Observations that the offspring of a cross made between the plants having two contrasting characters
shows only one character without any blending. - Self pollination of F offsprings.
- Cross pollination of parental generations.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 2. Observations that the offspring of a cross made between the plants having two contrasting characters shows only one character
without any blending.
Q2. Which of the following is a recessive trait of the garden pea plant?
- Full pod shape.
- Yellow seed colour.
- Terminal flower position.
- Green pod colour.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 3. Terminal flower position.
Q3. Which of the following traits studied by Mendel in garden pea is a dominant trait?
- Terminal flowers.
- Inflated pod.
- Green colour of seed.
- Yellow colour of pod.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 2. Inflated pod.
Q4. A heterozygous violet-flowered pea plant is crossed to another homozygous violet-flowered pea plant. What
percent of the progeny plants will have the recessive trait, i.e., white flowers?
- 0%
- 25%
- 50%
- 75%
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. 0%
Q5
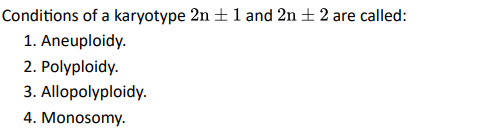
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. Aneuploidy.
Failure of segregation of chromatids during cell division cycle results in gain or loss of chromosome. This condition is called
aneuploidy.
Q6. Occasionally, a single gene may express more than one effect. The phenomenon is called:
- Multiple allelism.
- Mosaicism.
- Pleiotropy.
- Polygeny.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 3. Pleiotropy.
Occasionally, a single gene may express more than one effect. The phenomenon is called pleiotropy.
Q7. When ‘Aa’ is crossed with ‘aa’, (A is dominant over a):
- All the offspring will have dominant phenotype.
- All the offspring will have recessive phenotype.
- 50% of offspring will have dominant phenotype and 50% will have recessive phenotype.
- 75% of offspring will have dominant phenotype and 50% will have recessive phenotype.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 3. 50% of offspring will have dominant phenotype and 50% will have recessive phenotype.
Q8. In a dihybrid cross, if you get 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 ratio it denotes that:
- The allels of two genes are interacting with each other.
- It is a multigenic inheritance.
- It is a case of multiple allelism.
- The allels of two genes are segregating independently.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 4. The allels of two genes are segregating independently.
Q9. Mother and father of a person with ‘O’ blood group have ‘A’ and ‘B’ blood group respectively. What would be the
genotype of both mother and father?
- Mother is homozygous for ‘A’ blood group and father is heterozygous for ‘B’.
- Mother is heterozygous for ‘A’ blood group and father is homozygous for ‘B’.
- Both mother and father are heterozygous for ‘A’ and ‘B’ blood group, respectively.
- Both mother and father are homozygous for ‘A’ and ‘B’ blood group, respectively.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. Both mother and father are heterozygous for ‘A’ and ‘B’ blood group, respectively
Q10. The possibility of all genotypes of offspring in a genetic cross is calculated by a graphical representation which
was developed by:
- Kornberg.
- T.H. Morgan.
- Gregor Mendel.
- Reginald Punnett.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 4. Reginald Punnett.
Q11. For question two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason. Select the correct
answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
- Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- Assertion is true but reason is false.
- Both assertion and reason are false.
Assertion: Codominant alleles lack dominant recessive relationship.
Reason: Codominant alleles show incomplete dominance.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 3. Assertion is true but reason is false
Q12. Which of the following statements is the most appropriate for sickle cell anaemia?
- It cannot be treated with iron supplements.
- It is a molecular disease.
- It confers resistance to acquiring malaria.
- All of the above.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 4. All of the above.
Q13. From a cross AABb × aaBb, the genotypes AaBB : AaBb : Aabb will be obtained in the ratio:
- 1 : 1 : 2
- 1 : 2 : 1
- 2 : 1 : 1
- 2 : 1 : 2
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 2. 1 : 2 : 1
Q14. If a genetic disease is transferred from a phenotypically normal but carrier female to only some of the male
progeny, the disease is:
- Autosomal dominant.
- Autosomal recessive.
- Sex-linked dominant.
- Sex-linked recessive.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 4. Sex-linked recessive.
Sex-linked recessive disease- A genetic disease is transferred from a phenotypically normal but carrier female to only some of the
male progeny.
Q15. If a haemophilic woman marries a normal man:
- All their children will be normal.
- All their sons will be haemophilic.
- All their daughters will be haemophilic.
- 50% sons and 50% daughters will be haemophilic.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 2. All their sons will be haemophilic.
Q16. A woman with normal vision has a colorblind father. She marries a colourblind man. What proportion of their
children will be colourblind?
- 0%
- 25%
- 50%
- 100%
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 3. 50%
Q17. Two genes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are linked. In a dihybrid cross involving these two genes, the F heterozygote is crossed with
homozygous recessive parental type (aa bb). What would be the ratio of offspring in the next generation?
- 1 : 1 : 1 : 1.
- 9 : 3 : 3 : 1.
- 3 : 1.
- 1 : 1.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 4. 1 : 1.
Q18. In the F2 generation of a Mendelian dihybrid cross the number of phenotypes and genotypes are:
- Phenotypes – 4; genotypes – 16.
- Phenotypes – 9; genotypes – 4.
- Phenotypes – 4; genotypes – 8.
- Phenotypes – 4; genotypes – 9.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 4. Phenotypes – 4; genotypes – 9.
Q19. The inheritance pattern of a gene over generations among humans is studied by the pedigree analysis. Character
studied in the pedigree analysis is equivalent to:
- Quantitative trait.
- Mendelian trait.
- Polygenic trait.
- Maternal trait.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 2. Mendelian trait.
Q20. In a certain taxon of insects some have 17 chromosomes and the others have 18 chromosomes. The 17 and 18
chromosome-bearing organisms are:
- Males and females, respectively.
- Females and males, respectively.
- All males.
- All females.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. Males and females, respectively.
Q21. All genes located on the same chromosome:
- Form different groups depending upon their relative distance.
- Form one linkage group.
- Will not from any linkage groups.
- Form interactive groups that affect the phenotype.
Click To View The Answer
Ans: 1. Form one linkage group.
