Class 12 Chemistry The D and F-block Elements MCQs with answer
Sainik School provides Class 12 Chemistry MCQs focusing on “The D and F-block Elements,” offering students a comprehensive platform to master this important topic. These multiple-choice questions cover various aspects of the d-block and f-block elements, including their electronic configurations, properties, and applications in various fields.
Engaging with these MCQs allows students to deepen their understanding of the unique characteristics and trends exhibited by the d-block and f-block elements. Each MCQ is accompanied by accurate answer explanations, enabling students to thoroughly comprehend the underlying concepts and self-assess their understanding.
Practicing Class 12 Chemistry MCQs on “The D and F-block Elements” at Sainik School not only prepares students effectively for their exams but also equips them with essential analytical and problem-solving skills. Mastery of the d-block and f-block elements is crucial for a strong foundation in chemistry, benefiting students in their academic pursuits and future careers in science and technology.
Q1. Out of the following transition elements, the maximum number of oxidation states are shown by:
- Sc (Z = 21)
- Cr (Z = 24)
- Mn (Z = 25)
- Fe (Z = 26)
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 3. Mn (Z = 25)
Q2. Generally transition elements form coloured salts due to the presence of unpaired electrons. Which of the
following compounds will be coloured in solid state?

Click To View The Answers
Ans: 4. CuF2
Q3. Which of the following is amphoteric oxide?
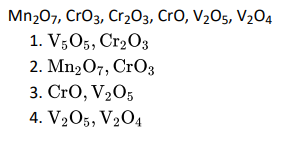
Click To View The Answers
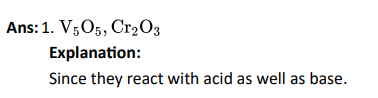
Q4. Generally transition elements and their salts are coloured due to the presence of unpaired electrons in metal
ions. Which of the following compounds are coloured?

Click To View The Answers

Q5. The magnetic nature of elements depends on the presence of unpaired electrons. Identify the configuration of
transition element, which shows highest magnetic moment.
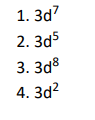
Click To View The Answers

Q6. Which of the following oxidation state is common for all lanthanoids?
- +2
- +3
- +4
- +5
Click To View The Answers

Q7. Which of the following will not act as oxidising agents?
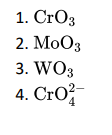
Click To View The Answers

Q8. Metallic radii of some transition elements are given below. Which of these elements will have highest density?
Element Fe Co Ni Cu
Metallic radii/pm 126 125 125 128
- Fe
- Ni
- Co
- Cu
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 4. Cu
Explanation:
On moving across the period in the periodic table the atomic radii of the element decreases towards right that is why density
increases towards right in a period.
Q9.

Click To View The Answers

Q10. There are 14 elements in actinoid series. Which of the following elements does not belong to this series?
- U
- Np
- Tm
- Fm
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 3. Tm
Q11. Transition elements form binary compounds with halogens. Which of the following elements will form MF3 type
compounds?
- Cr
- Co
- Cu
- N
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 1. Cr
- Co
Q12. Which of the following lanthanoids show +2 oxidation state besides the characteristic oxidation state +3 of
lanthanoids?
- Ce
- Eu
- Yb
- Ho
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 2. Eu
- Yb
Q13.

Click To View The Answers
Ans: 1. a, b
Q14. Why is HCl not used to make the medium acidic in oxidation reactions of KMnO4 in acidic medium?

Click To View The Answers

Q15. Although Zirconium belongs to 4d transition series and Hafnium to 5d transition series even then they show
similar physical and chemical properties because _.
- Both belong to d-block.
- Both have same number of electrons.
- Both have similar atomic radius.
- Both belong to the same group of the periodic table.
Click To View The Answers
Ans: 3. Both have similar atomic radius.
Explanation:
The almost identical radii of Zr (160pm) and Hf (159pm), a consequence of the lanthanoid contraction, account of their occurrence
together in nature and for the similar physical and chemical properties.
FAQs
How do MCQs on “The D and F-block Elements” in Class 12 Chemistry help students understand the unique properties and characteristics of transition and inner transition metals?
MCQs on “The D and F-block Elements” serve as valuable tools for Class 12 Chemistry students to grasp the distinctive properties and characteristics exhibited by transition and inner transition metals. These MCQs cover topics such as electronic configurations, magnetic properties, oxidation states, and complex formation of d-block and f-block elements. By engaging with these MCQs, students can deepen their understanding of the periodic trends and chemical behavior specific to these elements, enabling them to analyze and solve problems related to their properties and applications effectively.
What strategies can students employ to effectively prepare for Class 12 Chemistry exams using MCQs on “The D and F-block Elements”?
To effectively prepare for exams using MCQs on “The D and F-block Elements,” students should first ensure a solid understanding of the fundamental concepts and trends within these elements. They can then practice solving a variety of MCQs from reputable sources, focusing on different aspects such as electronic configurations, magnetic properties, and complex formation of transition and inner transition metals. It’s essential to analyze both correct and incorrect answers to deepen understanding and identify areas for improvement. Additionally, students can use MCQs to simulate exam conditions, helping them become familiar with the format and timing of the actual examination. Regular practice with MCQs, coupled with a comprehensive revision of concepts, can significantly enhance students’ performance in Class 12 Chemistry exams.
